Thesis: Frank Chen
Multi-Objective Spatial Optimization for Affordable Housing
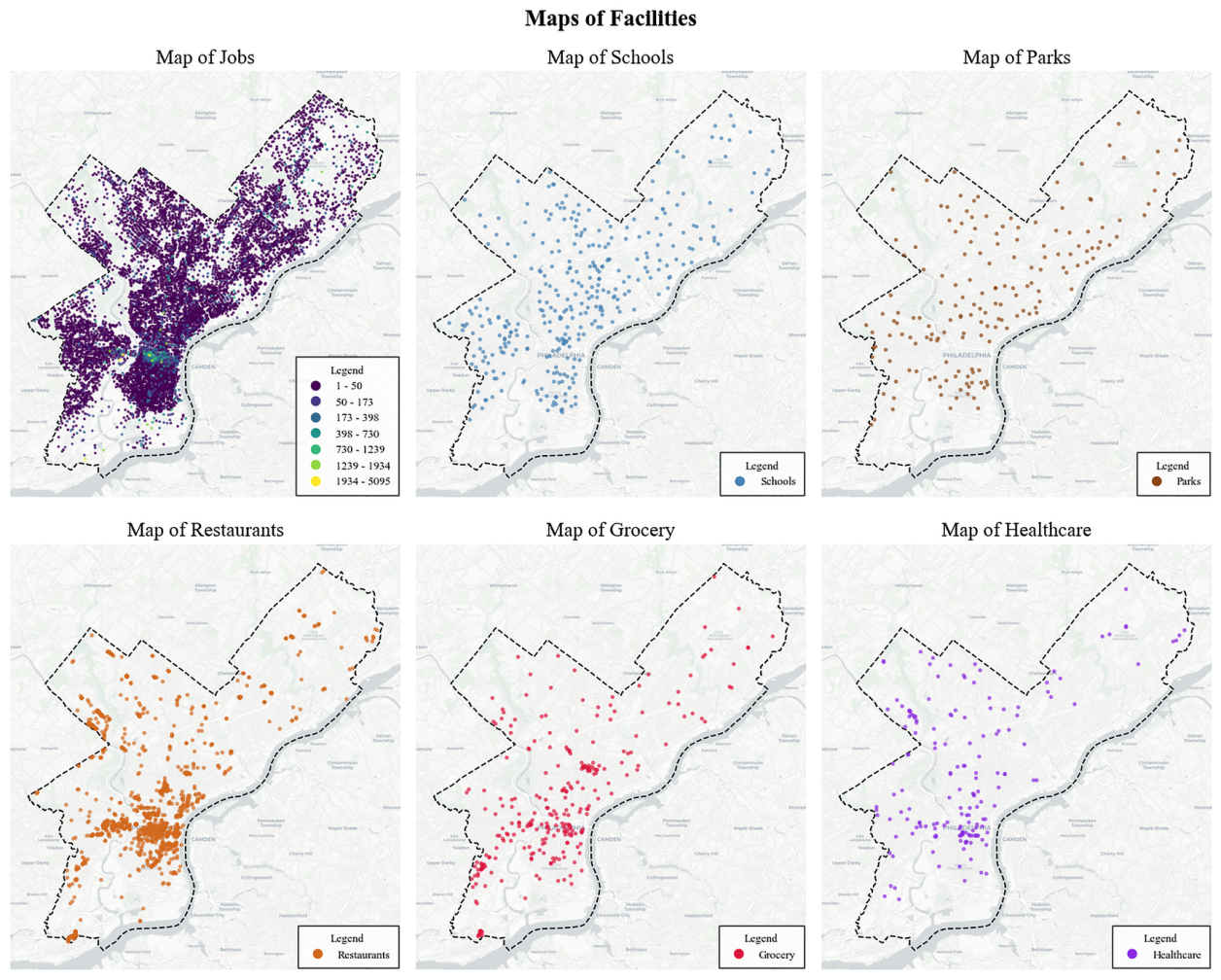
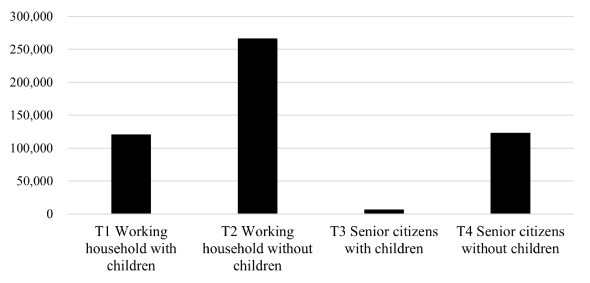
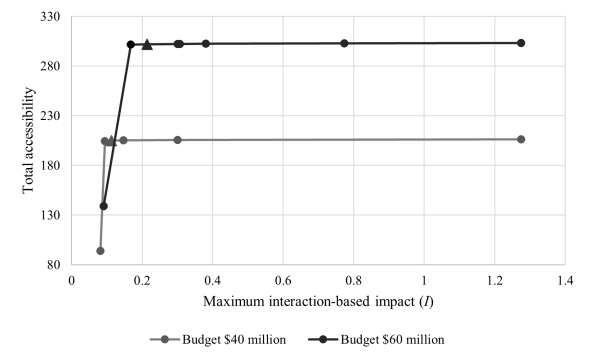
This study develops a multi-objective spatial optimization model for affordable housing siting that seeks to balance two key goals: maximizing accessibility to urban amenities and minimizing the perceived burden on host communities. The model integrates transit-based accessibility to jobs, schools, parks, grocery stores, restaurants, and healthcare facilities while accounting for public concerns about over-concentration of affordable housing. By incorporating a dispersion-based equity objective, the framework addresses the social and political dimensions of housing development. Constraints such as zoning, land use, and construction budgets are incorporated using parcel-level data for Philadelphia. The model allows for flexible weighting of objectives and facility types, enabling users to explore tradeoffs between accessibility and equity in a transparent, data-driven way.