Thesis: Jose Hernandez
Since Antiquity, reverberation and echo have been linked to monumental vaulted spaces. Classical Roman temples and medieval Gothic cathedrals produced a recognizable soundscape. This relationship was considered as natural as gravity. Vaults, domes, coves, pendentives, and other large concave surfaces produced a certain soundscape of reverberation and echo that enriched the medieval latin chant but was detrimental to the clarity of the modern Protestant sermon.
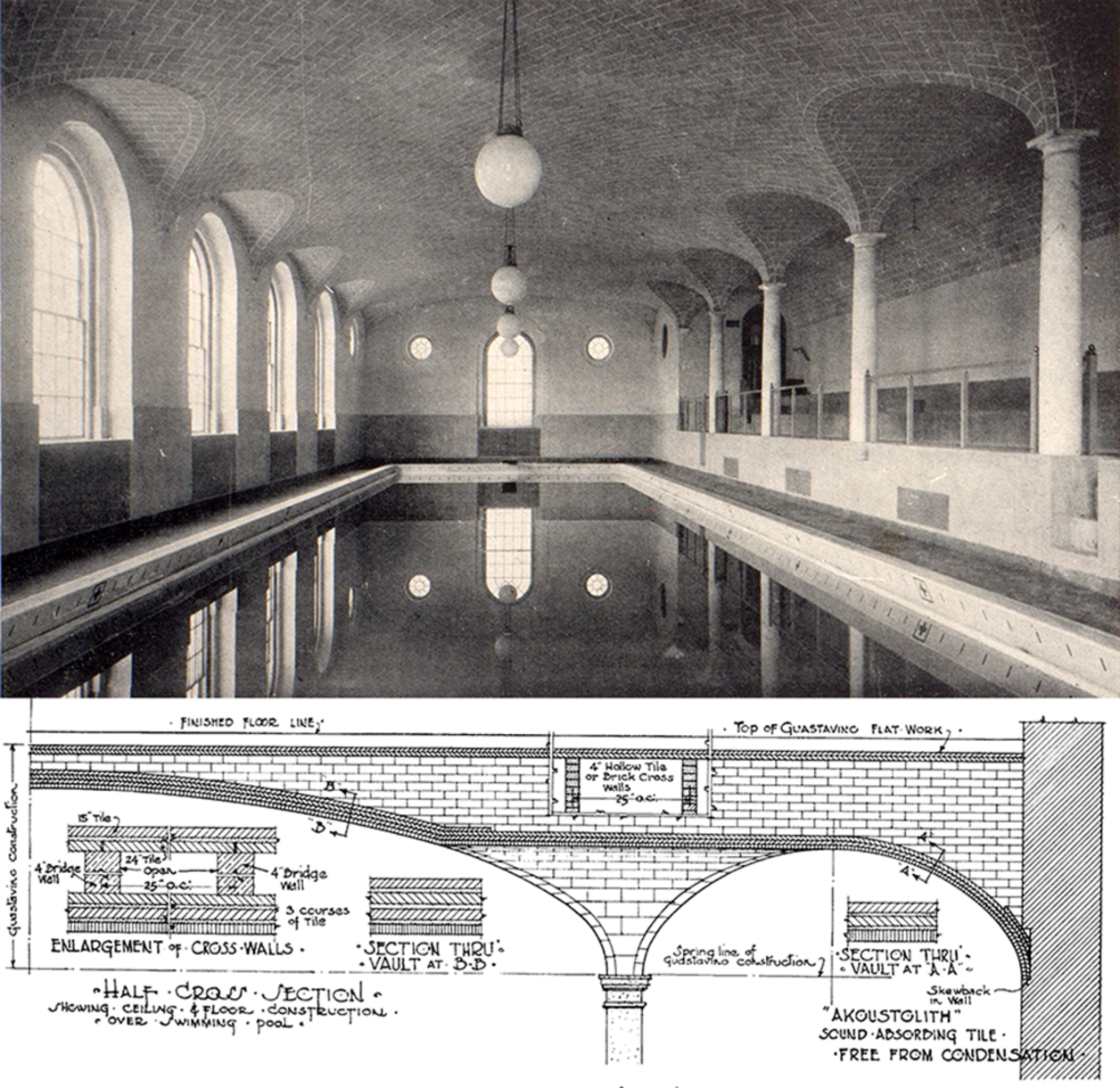
At the turn of the twentieth-century, Harvard professor Wallace Clement Sabine and master builder Rafael Guastavino Jr. responded to a demand to quiet Protestant churches designed in the Neo-Gothic style. Together, they patented an artificial stone that was structural, imitated traditional masonry, and absorbed the mid and high pitches. Branded as Akoustolith tile, the product was bonded to the self-supporting vaults of interlocking structural clay tiles that Guastavino popularized.
The Roaring Twenties marked a shift in the nature of the commissions with Akoustolith tile. They increasingly became secular and utilitarian: banks, auditoriums, libraries, museums, classrooms, courthouses, laboratories, gymnasiums, swimming pools, memorials, and railroad stations. Commissions ranged from the small music room at St. Mark’s school (Bigelow & Wadsworth, 1919) to the monumental Buffalo Central Terminal (Fellheimer & Wagner, 1929).
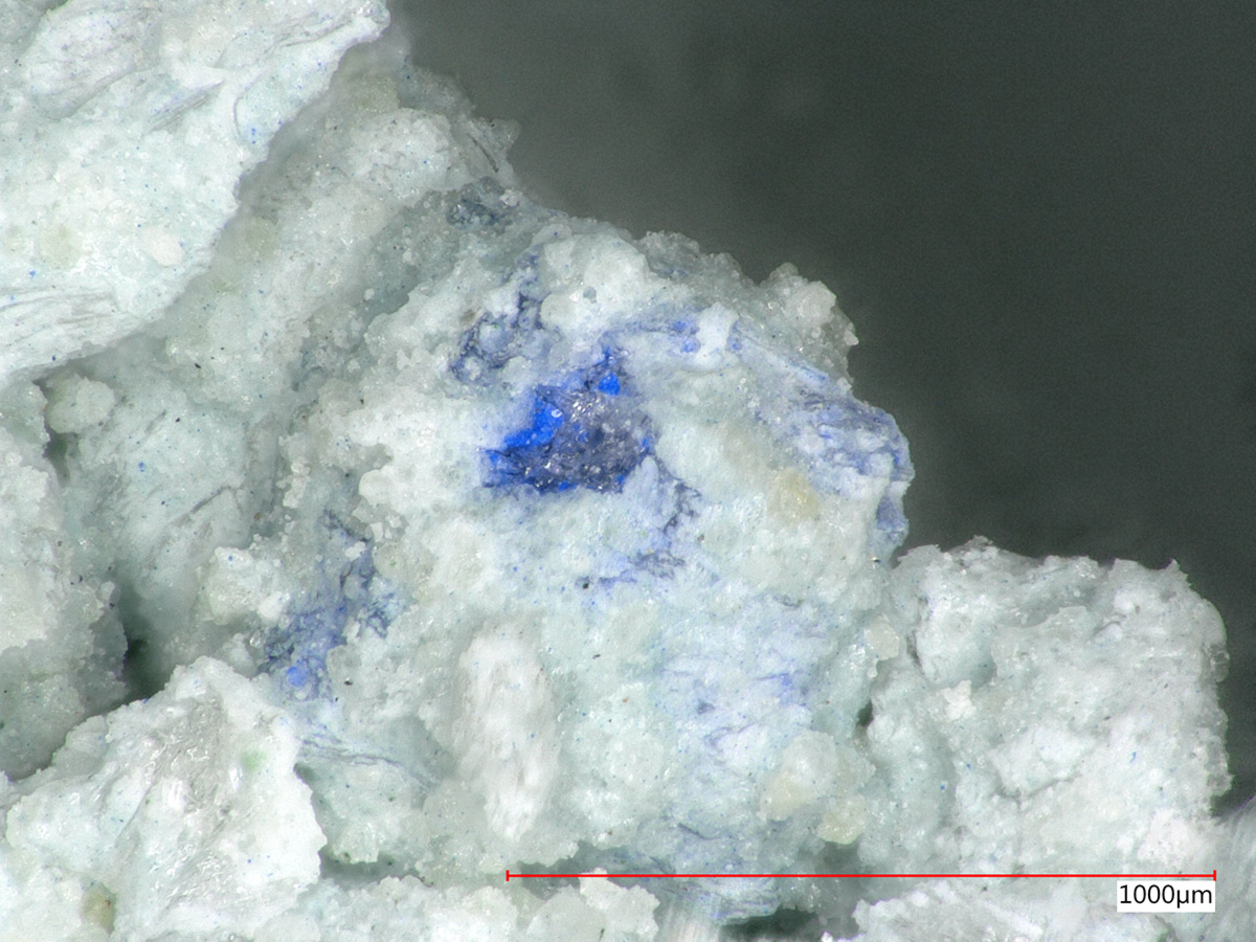
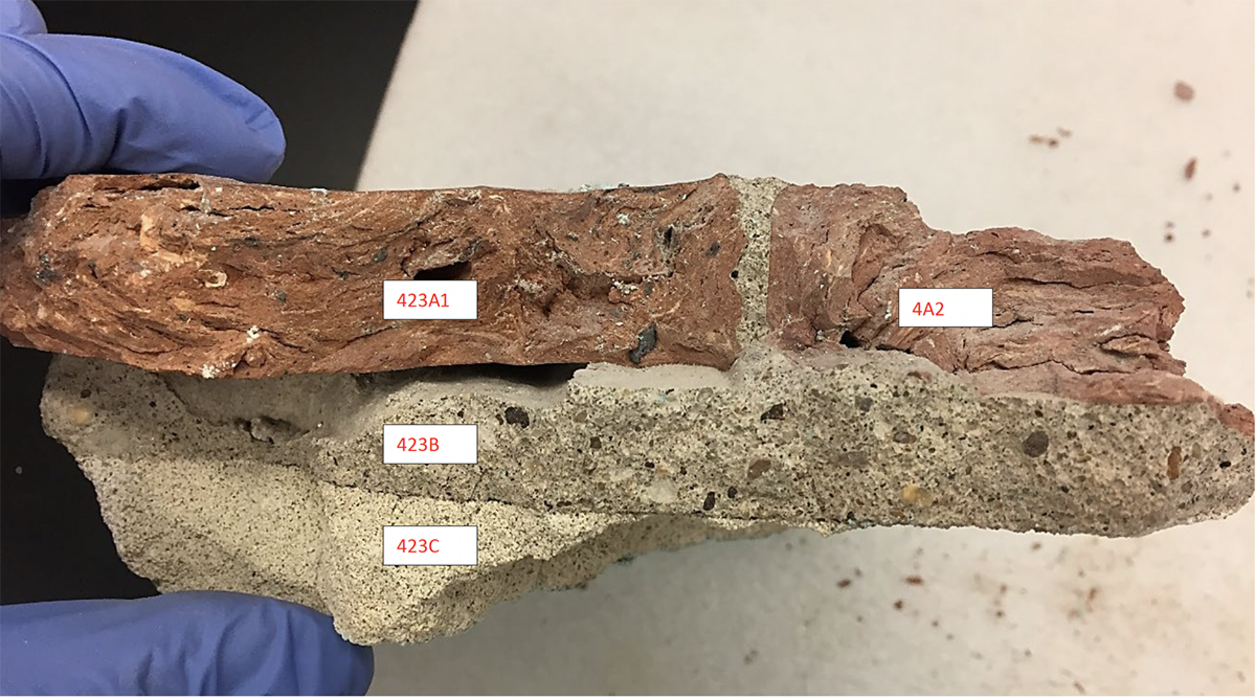
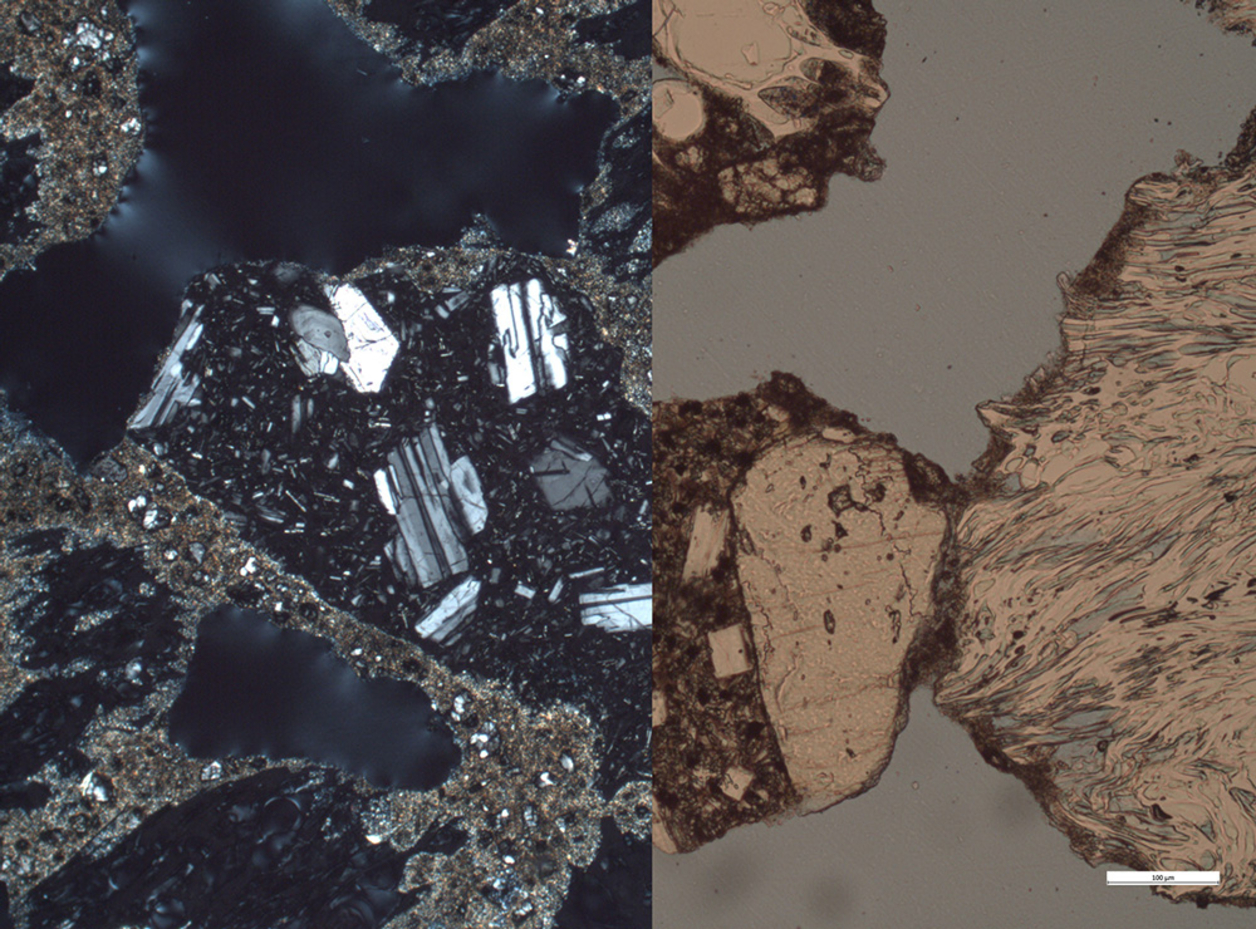
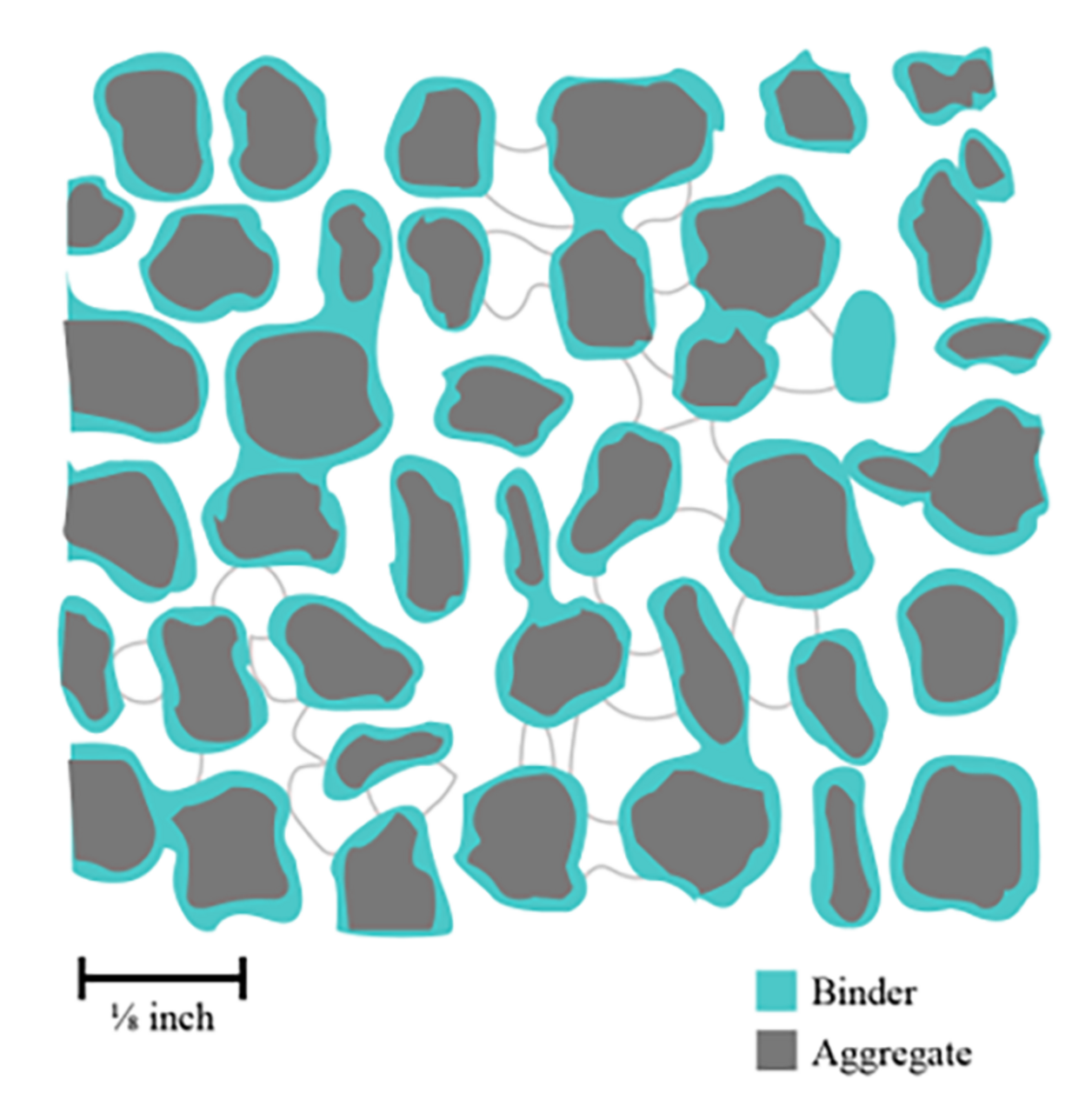
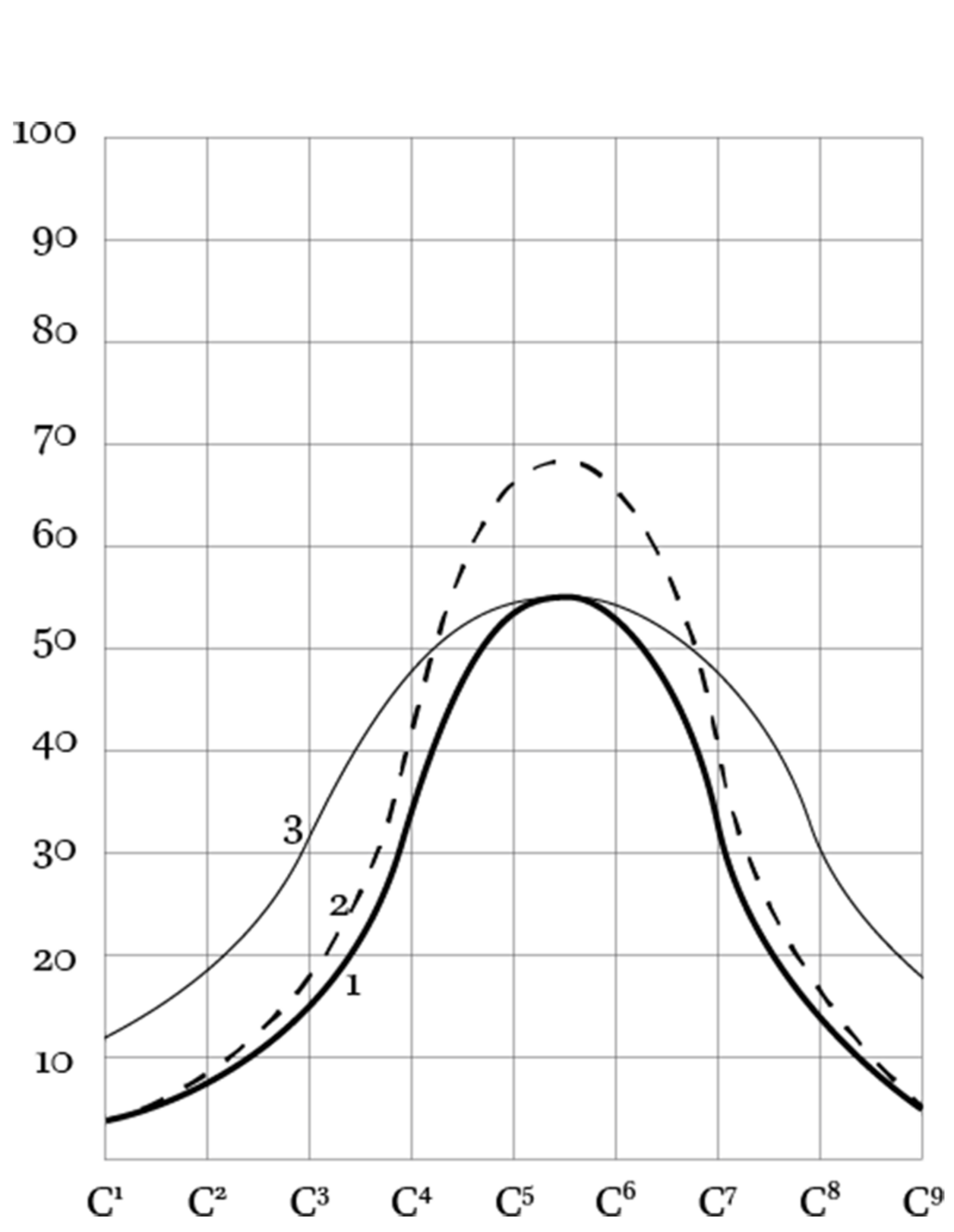
This thesis traces the origins and application of Akoustolith stone on more than 150 commissions and reviews the literature on the practice of sealing Akoustolith in churches and cathedrals. It argues that changes in composition modified its acoustical behavior by modulating particle size, angularity, sorting, and binder-to-aggregate ratio. It presents data on the petrographic, mechanical, and water absorption properties of specimens from 5 different commissions: the Nebraska State Capitol, the Washington National Cathedral, Buffalo Central Terminal, Nazareth Hall at University of Northwestern, Eglise de Notre Dame, and Cathedral of St. John the Divine.